What is Kaizen? Kaizen is an idea alluding to business exercises that ceaselessly work on all capabilities and include all representatives from the President to the sequential construction system laborers. Kaizen additionally applies to processes, for example, buying and coordinated operations, that cross authoritative limits into the production network.
Kaizen (Japanese: “continuous improvement”) is an idea alluding to business exercises and business types that consistently work on all capabilities and include all representatives from the Chief to the mechanical production system laborers. Kaizen additionally applies to processes, for example, buying and coordinated factors, that cross authoritative limits into the store network. It has been applied in medical services, psychotherapy, life training, government, and banking.
Recommended for reading: FMEA risk analysis tool
By working on normalized projects and cycles, kaizen expects to dispense with waste and redundancies (lean assembling). Kaizen was first polished in Quite a while after The Second Great War, impacted to a limited extent by American business and quality-administration educators, and most eminently as a feature of The Toyota Way. It has since spread all through the world and has been applied to conditions outside business and efficiency.

Contents
- 1 What is Kaizen?
- 2 Understanding the meaning of Kaizen
- 3 How does a Kaizen works?
- 4 How to implement Kaizen?
- 5 What are the benefits of Kaizen?
- 6 Kaizen and the PDCA Cycle
- 7 10 Principles of Kaizen and Kaizen pdf
- 8 Just-in-Time Inventory Strategy of Kaizen Technique
- 9 Examples of Kaizen
- 10 Kaizen Template Free Download [PDF/Excel/PPT]
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
- 11.1 What are the 5 elements of Kaizen?
- 11.2 What is the Kaizen method?
- 11.3 What is an example of Kaizen?
- 11.4 What are the main tools of Kaizen?
- 11.5 What is a Kaizen explain?
- 11.6 What are the 4 Kaizen principles?
- 11.7 What are the 3 Kaizen principles?
- 11.8 What are the 10 rules of Kaizen?
- 11.9 What are the facts about Kaizen?
- 11.10 What are the advantages of Kaizen?
- 11.11 What are the 8 wastes of Kaizen?
- 11.12 What is Kaizen in business?
- 11.13 What is Kaizen business model?
- 11.14 What businesses use Kaizen?
What is Kaizen?
Kaizen is a Japanese term meaning change for the better or continuous improvement. A Japanese business reasoning worries the cycles that ceaselessly further develop tasks and include all representatives. Kaizen considers improvement in efficiency to be a continuous and calculated process.
According to Masaaki Imai, Founder of Kaizen Institute, “Kaizen means improvement. Moreover, it means continuing improvement in personal life, home life, social life, and working life. When applied to the workplace Kaizen means continuing improvement involving everyone – managers and workers alike.”
There are 5 major Kaizen principles that are implanted in each Kaizen methodology and in each Kaizen conduct. These 5 principles are: Know your Customer, Let it Flow, Go to Gemba, Empower People and Be Transparent. The execution of these 5 principles in any organization is generally significant for an effective Continuous Improvement culture and to stamp a defining moment in the movement of value, efficiency, and work the board relations.
The idea of kaizen includes a great many thoughts. It includes making the workplace more proficient and powerful by making a group environment, working on ordinary strategies, guaranteeing representative commitment, and making some work seriously satisfying, less tiring, and more secure.
So, what is Kaizen meaning?
In short, a Kaizen is:
- Kaizen is a Japanese business theory that spotlights on bit by bit further developing efficiency and making a workplace more productive.
- Kaizen upholds change from any worker whenever.
- Kaizen means improve or constant improvement.
- Kaizen’s little changes can include quality control, in the nick of time conveyance, normalized work, the utilization of proficient hardware, and the end of waste.
- The Kaizen technique highlights the little changes presently can have enormous future effects and support.
Recommended for Reading:
Understanding the meaning of Kaizen
Over 30 years ago, Masaaki Imai sat down to pen the groundbreaking book ‘Kaizen: The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success’ (McGraw Hill). Through this book, the term Kaizen was introduced in the western world when the Toyota was completely focused on revolutionize the automotive industry with their Toyota Production System.
Today Kaizen is recognized worldwide as an important pillar of an organization’s long-term competitive strategy. Since introducing this term as a systematic approach for business improvement, and building business strategies, the companies that implement Kaizen have continually yielded superior results.
A portion of the critical goals of the kaizen reasoning incorporate quality control, without a moment to spare conveyance, normalized work, the utilization of productive gear, and the disposal of waste.
The general objective of kaizen is to roll out little improvements throughout some stretch of time to make enhancements inside an organization. That doesn’t mean adjustments happen gradually. The kaizen cycle just perceives that, the little changes presently can have colossal effects from here on out.
Upgrades can emerge out of any worker whenever. The thought is that everybody has a stake in the organization’s prosperity, and everybody ought to endeavor, consistently, to assist with making the plan of action better.
Many organizations have embraced the kaizen idea. Most prominently, Toyota utilizes the kaizen importance and reasoning inside its association. It regards kaizen as one of its fundamental beliefs. To further develop its creation framework, Toyota supports and engages all workers to recognize areas of likely improvement and make suitable arrangements.
Toyota’s process of identifying solutions is called “kaizen blitz.”
The Kaizen meaning is the “The Big Idea”. Make a culture of ceaseless improvement where all representatives are effectively taken part in working on the organization. Support this culture by putting together occasions zeroed in on working on unambiguous region of the organization.
Kaizen definition: Kaizen (continuous improvement) is a methodology where representatives at all levels of an organization cooperate proactively to accomplish customary, gradual upgrades to the assembling system. It might be said, it consolidates the aggregate gifts inside an organization to make a strong motor for development.
Since kaizen is more a way of thinking or the philosophy than a specific tool, its methodology is tracked down in various cycle improvement strategies, going from Total Quality Management (TQM) to the employee suggestion boxes. With kaizen, all workers are liable for recognizing holes and failures. What’s more, everybody, at each level in the association, proposes where enhancements can occur.
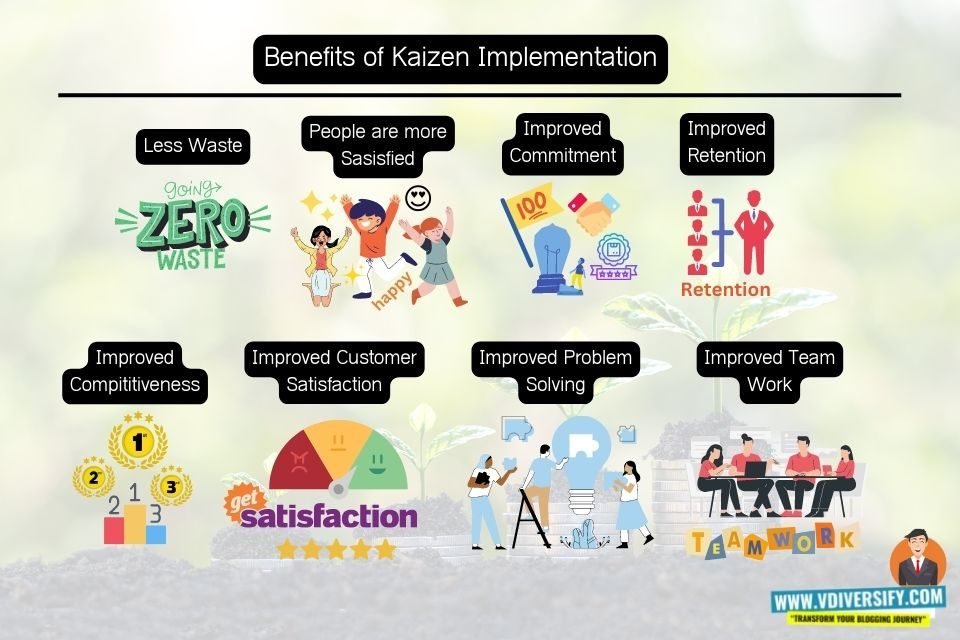
Kaizen aims for improvements in productivity, effectiveness and safety. However, individuals who follow this approach frequently open various advantages, as well, including:
- Less waste: Because of skilled employees, the inventory is used more efficiently
- People are more satisfied: Every employee in the organization plays his part in Kaizen event and they can create a direct impact on the way that things are done
- Improved commitment: Every team member feels that he is also part of something big and they highly pay attention towards their job and will contribute fully in their job role. With this they feel they have a stake in the job role that they are playing and takes the complete ownership of the job for 100% completion with zero errors
- Improved retention: satisfied and engaged people are more likely to stay.
- Improved competitiveness: Increases efficiency in work which in turn contributes to lower costs and higher-quality products
- Improved consumer satisfaction: With less customer defects, less errors during production, you can deliver high-quality products which in turn increases the overall customer satisfaction
- Improved problem solving: Employees can be able to concentrate better, dive deep into the topics, and work enabling the employees to solve problems continuously, efficiently, and effectively
- Improved teams: Working together in order to solve problems, participate, and contribute, helps in building great team work within the organization
How does a Kaizen works?
Kaizen includes five key standards: know your client, let it stream, go to Gemba (or the genuine spot, or the real place), engage individuals and be straightforward.
These five standards lead to three significant results: disposal of waste (additionally alluded to as monetary effectiveness), great housekeeping, and normalization. In a perfect world, kaizen turns out to be so imbued in an organization’s way of life that it at last becomes normal to representatives.
The kaizen significance sets that there is no ideal end and that everything can be refined. Individuals should endeavor to advance and improve continually.
The fundamental thought of kaizen is that individuals who play out specific errands and exercises know the most about them. Enabling those individuals to impact change is the best system for development. Collaboration is center to kaizen and teamwork is core to kaizen, where normal group gatherings are had including conversations about upgrades, changes, and tasks.

The Japanese word kaizen signifies ‘change for better’, with the inborn significance of either ‘nonstop’ or ‘reasoning’ in Japanese word references and in regular use. The word alludes to any improvement, once or persistent, enormous or little, in a similar sense as the English word improvement.
Notwithstanding, given the normal practice in Japan of naming modern or business improvement methods with the word kaizen, especially the practices led by Toyota, the word kaizen in English is regularly applied to measures for executing constant improvement, particularly those with a “Japanese way of thinking”.
The conversation underneath centers around such understandings of the word, as much of the time utilized with regards to current administration conversations.
Types of Kaizen:
Albeit the point of Kaizen is boundless social change, the occasions to launch the endeavors in question or spotlight on a particular arrangement of issues have developed.
In the West, these concentrated endeavors to roll out fast improvements to accomplish a momentary objective are many times the degree of Kaizen endeavors. There are various names related with Kaizen events, including Kaizen blitz, Kaizen workshop, Kaizen studio, focused improvement workshop, continuous improvement workshop and rapid process workshop. These events can depend on different apparatuses or center around unambiguous regions, for example, the 5S framework, complete useful upkeep and value stream planning.
However, in general, there are five types of Kaizen, and they are as follows:
- Point Kaizen
- System Kaizen
- Line Kaizen
- Plane Kaizen
- Cube Kaizen
Point Kaizen:
Point Kaizen is one of the most generally executed kinds of kaizen. It happens rapidly and typically absent any preparation. When something is found broken or wrong, speedy and prompt measures are taken to address the issues. These actions are for the most part little, detached and simple to carry out.; nonetheless, they can have an immense effect.
Now and again, it is likewise conceivable that the beneficial outcomes of point kaizen in one region can lessen or wipe out advantages of point kaizen in another space.
Instances of point kaizen incorporate a shop examination a wrecked by a boss materials or other little issues, and afterward requests the proprietor from the shop to play out a fast kaizen (5S) to redress those issues, or a line specialist who sees a possible improvement in proficiency by setting the materials required in one more request or nearer to the creation line to limit personal time.
System Kaizen:
System kaizen is achieved in a coordinated way and is contrived to address framework level issues in an association. It is an upper-level key arranging technique for a brief timeframe.
Line Kaizen:
Line Kaizen alludes to correspondence of enhancements between the upstream and downstream of an interaction. This can be stretched out in more than one way.
Plane Kaizen:
This is the following upper degree of line kaizen, in that few lines are associated together. In current wordings, this can likewise be depicted as a worth stream, where rather than conventional divisions, the association is organized into product offerings or families and worth streams. It very well may be envisioned as changes or upgrades made to one line being executed to different lines or cycles.
Cube Kaizen:
Cube kaizen depicts what is going on where every one of the places of the planes are associated with one another and no point is disconnected from some other. This would look like a circumstance where Lean has spread across the whole association. Enhancements are made all over through the plane, or upstream or downstream, including the total association, providers and clients. This could require a few changes in the standard business processes too.
How to implement Kaizen?
The Toyota Production System is known for kaizen, where all line staff are supposed to stop their moving creation line in the event of any irregularity and, alongside their boss, propose an improvement to determine the anomaly which might start a kaizen.
The cycle of kaizen movement can be characterized as: Plan → Do → Check → Act. This is otherwise called the Shewhart cycle, Deming cycle, or PDCA.
One more procedure utilized related to PDCA is the five whys, which is a type of main driver examination where the client requests a series from five “why” inquiries regarding a disappointment that has happened, putting together each ensuing inquiry with respect to the solution to the past. There are regularly a progression of causes coming from one main driver, and they can be pictured utilizing fishbone charts or tables. The five whys can be utilized as a primary device in private improvement, or as a way to make riches.
Masaaki Imai put the term on the map in his book Kaizen: The Way into Japan’s Cutthroat Achievement.
In the Toyota Way Fieldbook, Liker and Meier examine the kaizen rush and kaizen burst (or kaizen occasion) ways to deal with nonstop improvement. A kaizen rush, or fast improvement, is a centered movement around a specific cycle or action. The fundamental idea is to distinguish and immediately eliminate squander. Another methodology is that of the kaizen burst, a particular kaizen action on a specific cycle in the worth stream. Kaizen facilitators by and large go through preparing and certificate prior to endeavoring a Kaizen project.
During the 1990s, Teacher Iwao Kobayashi distributed his book 20 Keys to Work environment Improvement and made a functional, bit by bit improvement system called “the 20 Keys”. He recognized 20 tasks center regions which ought to be improved to accomplish comprehensive and manageable change. He went further and recognized the five degrees of execution for every one of these 20 center regions. Four of the center regions are called Establishment Keys. As per the 20 Keys, these establishment keys ought to be sent off in front of the others to frame areas of strength for an in the organization. The four foundation keys are:
- Key 1 – Cleaning and Organizing to Make Work Easy, which is based on the 5S methodology.
- Key 2 – Goal Alignment/Rationalizing the System
- Key 3 – Small Group Activities
- Key 4 – Leading and Site Technology
How to implement Kaizen?
Kaizen can be carried out and implemented in a seven-step cycle to establish an environment in the light of nonstop improvement. This efficient technique incorporates the following steps.
7 steps to implement Kaizen:
1. Step 1: Get employees involved
2. Step 2: Gather list of problems
3. Step 3: Encourage solutions and choose an idea
4. Step 4: Test the solution
5. Step 5: Regularly measure and analyze the results
6. Step 6: If successful adopt the solution
7. Step 7: Repeat on an ongoing basis
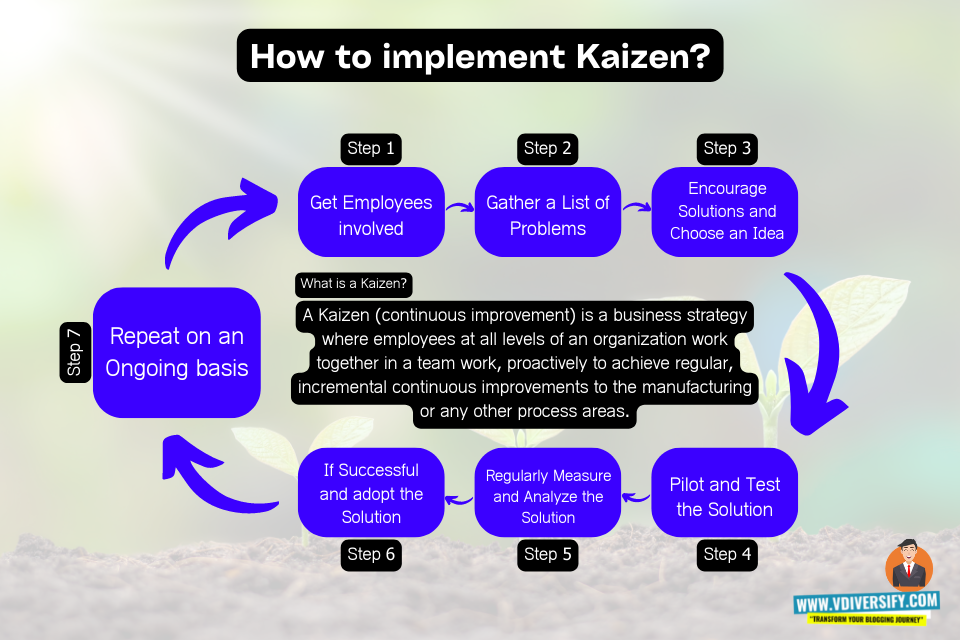
Step 1: Get employees involved
Look for the contribution of workers or employees, incorporating requesting their assistance in distinguishing issues and issues. Doing so makes purchase in for change. Frequently, this is coordinated as unambiguous gatherings of people accused of get-together and handing-off data from a more extensive gathering of workers or employees.
Step 2: Gather list of problems
Utilizing broad input from all representatives, assemble a rundown of issues and possible open doors. Make a rundown on the off chance that there are many issues.
Step 3: Encourage solutions and choose an idea
Urge representatives to offer clever fixes, and creative solutions, with every possible kind of thoughts empowered. Pick a triumphant arrangement or arrangements from the thoughts introduced.
Step 4: Test the solution
Implement and execute the best award-winning solution above, with everybody’s participation in the roll-out. Make experimental runs of projects, try out and run pilots, or find other small steps to try out and test the solution.
Step 5: Regularly measure and analyze the results
At different stretches, and at regular intervals, really look at the progress, with explicit plans, layouts, and designs for who will be the resource and how best to keep ground-level specialists locked in. Decide how effective the change has been.
Step 6: If successful adopt the solution
Once the solution is found successful, now its time to adopt the same solution through out the organization. If possible and necessary, in the implementation steps of the solution can be slightly altered in order to get the best results for that process area.
Step 7: Repeat on an ongoing basis
The seventh step is all about repeating the above 6 steps on a consistent ongoing basis to get the best results. Aim should be towards finding more solutions to the problems that get generated in that process area. New problems to be listed on the board, and solutions to be brought in for better improvements.
The dual nature of the Kaizen system:
Kaizen is part activity plan and part philosophy.
As an activity plan, Kaizen is tied in with putting together occasions zeroed in on working on unambiguous regions inside the organization. These occasions include groups of workers at all levels, with a particularly amazing accentuation on including plant floor representatives.
As a part philosophy, Kaizen is tied in with building a culture where all workers are effectively participated in recommending and executing upgrades to the organization. In real lean organizations, it turns into a characteristic perspective for the two chiefs and plant floor workers.
Kaizen works inseparably with Normalized Work. Normalized Work catches the ongoing prescribed procedures for a cycle, and Kaizen expects to track down enhancements for those cycles. Note the accentuation on current; Normalized Work is living documentation (it persistently advances through Kaizen).
Kaizen Events:
A common Kaizen event has a cycle and process that resembles this:
- Put forth goals, objectives and give any important foundation
- Survey the present status and foster an arrangement for upgrades
- Execute enhancements and implement improvements
- Review, audit, and fix what doesn’t work
- Report results and decide any subsequent things
The Kaizen Philosophy:
Strangely, Kaizen as an activity plan is precisely exact thing creates Kaizen as a way of thinking. At the point when Kaizen is applied as an activity plan through a reliable and supported program of fruitful Kaizen occasions, it helps representatives to ponder their work. At the end of the day, predictable use of Kaizen as an activity plan makes colossal long haul esteem by fostering the way of life that is required for genuinely compelling nonstop improvement.
Kaizen 5S framework
A 5S framework is a basic piece of the Kaizen framework and lays out an optimal actual working environment. The 5S’s center around making visual request, association, neatness and normalization to further develop benefit, effectiveness, administration and security. The following are the first Japanese 5S’s and their normal English interpretations.
- Seiri/Sort (organize). Separate necessary workplace items from unnecessary ones and remove unnecessary items.
- Seiton/Set in order (create orderliness). Arrange items to allow for easy access in the way that makes the most sense for work.
- Seiso/Shine (cleanliness). Keep the workspace clean and tidy.
- Seiketsu/Standardize (standardized cleaning). Systematize workplace cleanup best practices.
- Shitsuke/Sustain (discipline). Keep the effort going.
What are the benefits of Kaizen?
Kaizen offers organizations numerous significant advantages. Some of them are:
- Greater staff satisfaction
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Reduction in staff turnover
- Strengthened employee loyalty
- Lower costs
- Greater efficiency and productivity
- Better problem solving
Let us also go deeper and understand about the advantages and disadvantages of a Kaizen.
Kaizen Advantages:
- Kaizen emphasis on progressive improvement can make a gentler way to deal with change rather than large endeavors that might be deserted because of their propensity to incite change obstruction and pushback.
- Kaizen supports investigation of cycles so that missteps and waste are diminished.
- With less mistakes, oversight and assessment needs are limited.
- Representative resolve improves on the grounds that Kaizen supports a feeling of significant worth and reason.
- Cooperation increments as representatives suspect past the particular issues of their area of expertise.
- Client center extends as workers become more mindful of client necessities.
- Frameworks are set up to guarantee enhancements are energized both in the short and long terms.
Kaizen Disadvantages:
- Organizations with societies of territorialism and shut correspondence may initially have to zero in on social changes to establish a responsive climate.
- Momentary Kaizen occasions might make an explosion of fervor that is shallow and brief and, hence, isn’t supported.
Kaizen and the PDCA Cycle
Upgrades for the most part follow the PDCA cycle design. PDCA represents Plan-Do-Check-Act. The Arrangement segment incorporates proposing and delineating changes so everybody knows what’s in store when groups attempt to take care of an issue.
The Do organize carries out the best answer for the issue. The Check step includes assessing the answer for the issue to check whether it worked.
At the point when an organization Acts, it decides if the arrangement ought to turn into an organization standard or on the other hand in the event that it needs further changes. In the event that directors choose to carry out additional changes, kaizen returns to the Arrangement step and the cycle begins once again.
10 Principles of Kaizen and Kaizen pdf
Since executing Kaizen requires empowering the right mentality all through an organization, 10 rules that address the Kaizen outlook are normally referred to as center to the way of thinking. They are:
1. Let go of the assumptions
2. Be proactive about taking care of issues and solving problems
3. Try not to acknowledge business as usual
4. Let go of perfectionism and take a demeanor of iterative, versatile change
5. Look for solutions as and when you find mistakes
6. Establish and create an environment wherein everybody feels engaged to contribute
7. Try not to acknowledge the obvious issue; instead, ask “why” multiple times at least five times to get to the underlying root cause
8. Gather information and make sure to consider opinions from multiple people
9. Use creativity and inventiveness to track down minimal expense and find low-cost, small improvements
10. Improve constantly and never stop the eagerness to improve on something

You can download the Kaizen pdf from here: 10 principles of Kaizen pdf. Apart from this, in general there are 4 types of Kaizen principles that everyone must know. Here are the types of Kaizen principles:
1. The Kaizen Teian: Bottom-Up Improvement
2. Kaizen Events: Defined Improvements
3. Kaikaku: Radical Change
4. Kakushin: Break-through Innovation
Kaizen Teian: Bottom-Up Improvement
Kaizen Teian portrays a type of progress where individuals take an interest to work on their own cycles. This base up kind of Kaizen drives a social change since it expects everybody to contemplate improvement consistently, all over the place. At its center, Kaizen Teian is about effectively affecting all individuals in progress. To set out in making a constant improvement culture in your association, you ought to begin with Kaizen Teian.
Kaizen Teian supports each individual from the labor force, from initiative to cutting edge laborers, to propose changes that can further develop work process. The thought is that those specialists who are in the gemba, or genuine spot, are those bound to recognize genuine open doors for working on the progression of their cycles.
Kaizen Events: Defined Improvements
Dissimilar to everyday Kaizen, a Kaizen event isn’t about ceaseless improvement — it’s about a particular cycle improvement created throughout a concise measure of time.
Kaizen events are normally short, engaged improvement projects where individuals, including the supervisory crew, take part in breaking down their Value Stream Map (VSM) to tackle a particular issue. While everyday Kaizen events might be little in scope or to some degree unconstrained, a Kaizen event requests smart preparation by group pioneers included. These events could keep going for a few days or even weeks, and target explicit difficulties that, once tackled, could prompt a stage change in productivity, quality or execution.
Obviously, all occasions should be lined up with more extensive functional objectives and cycles to have a supported effect.
Kaikaku: Radical Change
Some of the time little changes aren’t sufficient to drive the upgrades an association should be serious. That is the point at which now is the right time to go to Kaikaku.
Not at all like Kaizen, which centers around steady changes, Kaikaku portrays an interaction where a whole association is centered around an extreme cycle change. Instead of working on a cycle, Kaikaku might request the association moves to a completely new interaction. Instances of Kaikaku could incorporate moving from manual to robotized creation or setting out on a computerized change that drives work environment joint effort.
Kakushin: Break-through Innovation
In the event that Kaikaku is progressive, Kakushin is down evolving. Kakushin happens when you move to a completely better approach for following through with something. It’s about the huge advancement that makes a huge difference.
While Kaikaku could mean rolling out a significant improvement in how things are finished, Kakushin may be tied in with changing what is finished. For instance, assuming that Kaikaku is tied in with moving from manual to mechanized creation, Kakushin would be the change to 3D printing those materials, requesting new abilities from the labor force.
Kakushin requests the executives challenge their suspicions about why they carry on with work a specific way. It will require a culture change that can focus on a better approach for getting things done. Conceptualizing and examination are the devices of Kakushin.
Just-in-Time Inventory Strategy of Kaizen Technique
One of the critical objectives of the kaizen cycle is to decrease waste and increment productivity in the creation cycle. An in the just-in-time (JIT) stock system permits the board to limit overabundance stock by coordinating the conveyance of unrefined components from providers with creation plans.
The JIT methodology is otherwise called the Toyota Production System (TPS), for the organization that promoted it, JIT assists organizations with reducing expenses since producers don’t need to pay stock conveying costs. It likewise decreases squander in light of the fact that organizations are not left with additional stock should a client drop or delay a request.
Kanban is a stock control framework utilized related to a JIT methodology. It gives workers obvious signals that let them know the time has come to arrange parts and materials as they run out.
The framework depends on hued cards that track creation and ready workers when now is the right time to recharge a required part or material. It empowers representatives to rapidly arrange the right number of parts from the provider and have them conveyed to where they are required in the plant.
The objective of kanban is to guarantee the effective running of the processing plant sequential construction system and to keep bottlenecks from happening.
Examples of Kaizen
Toyota is apparently the most well-known for its utilization of Kaizen, however different organizations have effectively utilized the methodology. The following are three models as Kaizen examples:
Lockheed Martin:
The aviation organization is a notable defender of Kaizen. It has utilized the technique to effectively lessen producing expenses, stock and conveyance time.
Ford Motor Company:
At the point when lean aficionado Alan Mulally became President of Passage in 2006, the automaker was near the very edge of chapter 11. Mulally utilized Kaizen to execute quite possibly of the most renowned corporate circle back ever.
Pixar Animation Studios:
Pixar applied the nonstop improvement model to lessen the dangers of costly film disappointment by utilizing quality control checks and iterative cycles.
Kaizen Template Free Download [PDF/Excel/PPT]
Kaizen means “Continuous Improvement”. Know matter what type of business or an organization you are running, implementing a Kaizen in your work area is going to give you lots of benefits, which helps you grow your organization immensely. If you are looking for a Kaizen template, then you can download the same from this link below:
Kaizen Template PDF free download:
Kaizen Template Excel free download:
Kaizen Template PPT free download:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What are the 5 elements of Kaizen?
The five kaizen components, elements, principles, or standards are: know your client, let it flow, go to Gemba, empower people, and be transparent. Individuals additionally in some cases ask what kaizen 5S alludes to. It’s a cycle frequently utilized in lean assembling and connects with five stages of progress: Sort, Straighten, Sweep, Standardize, and Sustain. A 5S event follows every one of these means each day in turn.
What is the Kaizen method?
It’s a business reasoning with core values and devices that looks to include all representatives in the steady and consistent improvement of different region of an organization. The kaizen technique centers around connecting with representatives and utilizing cooperation to establish an effective and charming workplace.
What is an example of Kaizen?
Toyota is a well-known illustration of an organization utilizing kaizen to support its prosperity. One more ordinarily known illustration of kaizen in real life includes Portage Engine Organization, which embraced kaizen to slice the time it took to finish different assembling processes.
What are the main tools of Kaizen?
The Kaizen philosophy utilizes various instruments relying upon the objective. For example, the 5S device is in many cases utilized in lean assembling and to guarantee that working environments are effective, useful, and safe. JIT and Kanban are utilized for stock control. The five whys (what, when, where, why, and who) is an instrument used to uncover the underlying driver of an issue. Esteem stream planning is a logical device that is utilized to distinguish spots to wipe out squander. Follow-up occasions are devices used to support enhancements.
What is a Kaizen explain?
Kaizen is a continuous improvement tool and a term of two Japanese words that together gives the meaning as “good change” or “improvement.” Nonetheless, Kaizen has come to imply “continuous improvement” through its relationship with lean technique and standards.
What are the 4 Kaizen principles?
When it comes to understanding the 4 Kaizen principles, here are the below listed ones which will give you an overview of principles of Kaizen. The 4 Kaizen principles are divided into 4 types of Kaizen which are defined as follows:
1. The Kaizen Teian: Bottom-Up Improvement
2. Kaizen Events: Defined Improvements
3. Kaikaku: Radical Change
4. Kakushin: Break-through Innovation
What are the 3 Kaizen principles?
The 3 principles of Kaizen are: gemba: the place where work is done. gembutsu: the actual product. genjitsu: the facts.
What are the 10 rules of Kaizen?
The 10 rules of Kaizen can be read as listed below:
1. Start with the 3 “Actual” Rule
- Go to the place where the process is performed;
- talk to the people involved;
- observe and chart the actual process.
2. Abolish the old and conventional concepts
3. Question current practices and reject the status quo
4. Rely on data, not opinions
5. Correct mistakes immediately
6. Don’t seek perfection, choose a simple solution
7. Ask why 5 times to identify root causes
8. Value creativity and wisdom before capital
9. Seek out the knowledge of more than just one person
10. Continuously and consistently improve
What are the facts about Kaizen?
The below listed facts are the facts of Kaizen:
- Kaizen is a way of thinking that upholds constant, steady cycle changes that support an elevated degree of effectiveness.
- It can assist you with further developing the manner in which you work actually, by wiping out different sorts of “squander.”
- Kaizen can likewise be an association wide methodology that saddles ideas and backing from individuals at each level.
- Wide interest can further develop confidence and fulfillment, as well as creation, costs, and other hard measures.
- Utilized well, a kaizen approach uncovers what a major effect little changes can make.
What are the advantages of Kaizen?
Kaizen is tied in with diminishing waste by wiping out overproduction, improving quality, being more productive, and efficient, having less idle time, and decreasing non-value added activities. All of these may lead to an expense investment funds, and can transform likely misfortunes into benefits.
What are the 8 wastes of Kaizen?
The kaizen reasoning was created to further develop producing cycles, and one of the components prompted the progress of Japanese assembling through excellent and low expenses. Notwithstanding, you can acquire the advantages of the kaizen approach in numerous other work spaces, both on an individual level and for your entire group or association.
A significant part of the spotlight in kaizen is on diminishing, eliminating, and reducing the “waste,” and this waste takes a few structures. The wastes of Kaizen can be termed into, “TIMWOODS” and they can be defiend as follows:
- T: Transportation
- I: Inventory
- M: Motion
- W: Waiting
- O: Overproduction
- O: Over-processing
- D: Defects
- S: Skills
And the 7 wastes of Kaizen term are, transportation, inventory, motion, waiting, overproduction, over-processing, and defects.
What is Kaizen in business?
In business, the term Kaizen is nothing but continuous improvement. Kaizen is a way to deal with making continuous improvement in light of the possibility that little, progressing positive changes can procure critical enhancements. Commonly, it depends on collaboration and responsibility and stands as opposed to approaches that utilization revolutionary or hierarchical changes to accomplish change.
What is Kaizen business model?
What is the Kaizen model? A Kaizen business model (continuous improvement) is a business strategy where employees at all levels of an organization work together in a team work, proactively to achieve regular, incremental continuous improvements to the manufacturing or any other process areas. In a sense, it combines the collective talents within a company to create a powerful ideas and solutions for improvement.
What businesses use Kaizen?
Kaizen is being used by many businesses all over the world. The Kaizen is most popular among the organizations that are focused on manufacturing, software development, telecommunication, lean IT, and service improvement.
Kaizen is not unique to any manufacturing industry, or to the tech industry, as the business strategy of Kaizen has already been employed in many well-known industries such as healthcare, semiconductor, IT, psychology, government, mining, aerospace, life-coaching, and banking as a way to improve their business processes, decision-making, and logistics to ease the way of working and to make an impact in everyone’s livelihoods.

“Hey, I am Sachin Ramdurg, the founder of VDiversify.com.
I am an Engineer and Passionate Blogger with a mindset of Entrepreneurship. I have been experienced in Blogging for more than 15+ years and following as a youtuber along with blogging, online business ideas, affiliate marketing, and make money online ideas since 2012.

3 thoughts on “What is Kaizen? | Best Business Strategy for Continuous Improvement?”